Fast Delivery And Low MOQ With Money Back Guarantee...
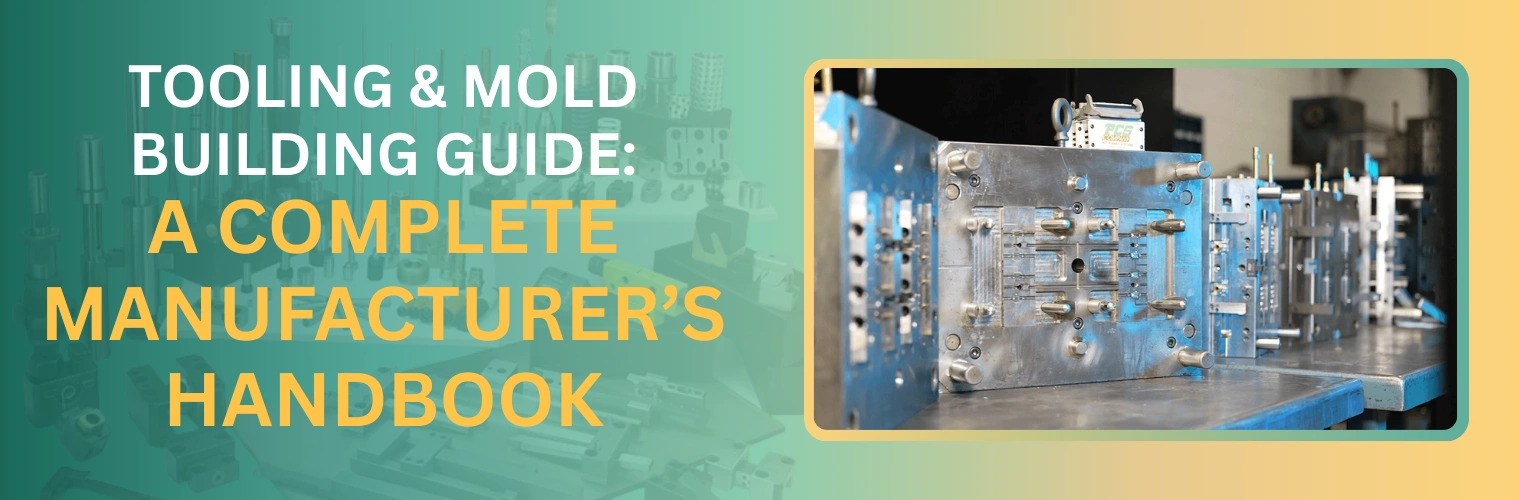
Tooling and mold building are the backbone of high-quality plastic part manufacturing. A well-designed mold ensures accuracy, repeatability, and efficiency throughout the injection molding process.
Understanding each stage of this Tooling & Mold Building Guide helps designers, engineers, and manufacturers reduce defects, optimize performance, and achieve long-term cost savings. Mold design directly impacts cycle time, part strength, surface finish, and overall manufacturing quality.
The mold is the most critical and expensive component in injection molding. A strong and precisely built mold ensures consistent manufacturing while reducing scrap and downtime. Designers must consider material properties, part geometry, cooling efficiency, and tool life during the early planning phase.
Important factors to analyze:
A clear understanding of these factors ensures better manufacturing outcomes.
Mold types differ based on application, cost, and production requirements. Selecting the right one is essential for performance and efficiency.
Common mold types:
Each mold type has unique benefits depending on the manufacturing strategy.
Choosing the right mold material determines durability, cycle time, and maintenance needs. Mold materials must withstand high temperatures, pressure, and abrasive plastic resin additives.
Common mold materials:
The selection depends on part complexity, surface finish requirements, and expected manufacturing volume.
Mold design requires accuracy and attention to detail. Engineers use advanced software to simulate plastic flow, cooling patterns, and potential defects before manufacturing begins.
Key design considerations:
A strong design foundation ensures fewer manufacturing issues later.
After design approval, mold fabrication begins. Modern manufacturing techniques help achieve tight tolerances and smooth surfaces.
Common fabrication methods:
Using the right machining techniques ensures accuracy and long-lasting performance.
Cooling plays a vital role in the injection molding cycle. Poor cooling design can result in long cycle times, warpage, or dimensional inaccuracies.
Important cooling features:
Efficient cooling leads to faster cycle times and improved part consistency.
After cooling, parts must be released smoothly without damage. A proper ejection system ensures dimensional stability and a clean finish.
Common ejection methods:
Correct ejection planning prevents sticking, drag marks, and part deformation.
Before full-scale manufacturing, molds undergo testing to ensure all features function correctly. This stage reduces risk and identifies necessary adjustments.
Typical testing steps:
Testing ensures the mold meets all project requirements before final approval.
Regular maintenance increases mold lifespan and ensures consistent production quality. Neglecting maintenance can lead to defects, downtime, and expensive repairs.
Maintenance tasks include:
Scheduled maintenance protects the mold and ensures smooth operations.
Mold building is a significant investment, but proper planning helps control costs while maintaining quality.
Cost contributors:
Maintaining a balance between budget and performance ensures the best results with long-term value.
Tooling and mold building support a wide variety of industries because of their precision and versatility.
Common applications:
The demand for reliable tooling continues to grow across global markets.
A strong understanding of mold design, tooling materials, advanced molding methods, and testing ensures efficient and reliable manufacturing. This Tooling & Mold Building Guide provides manufacturers with the knowledge needed to optimize mold performance, reduce defects, and enhance product quality. Investing in proper tooling is essential for long-term manufacturing success.
Need Expert Mold Building Assistance? (CTA)
For tooling design, mold development, or production support, contact our expert team today: : +1(917)-993-9690 or info@plastic-injectionmolding.com

