Fast Delivery And Low MOQ With Money Back Guarantee...
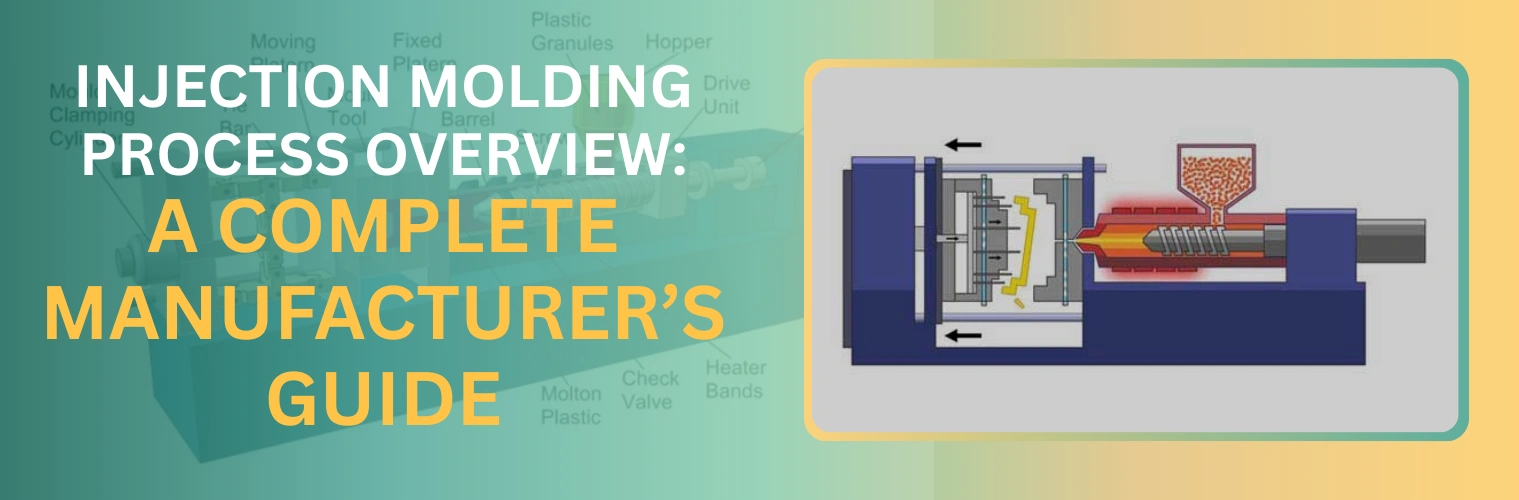
Injection molding is one of the most efficient, versatile, and reliable manufacturing methods used across industries today. It allows businesses to manufacture high-volume plastic parts with exceptional accuracy, smooth surface finishes, and repeatable quality.
A detailed Injection Molding Process Overview helps engineers, designers, and manufacturers understand each stage of the cycle so they can avoid manufacturing issues and create better-performing products.
The injection molding process involves converting solid plastic pellets into finished molded parts using heat, pressure, and controlled cooling. The workflow is systematic and repeatable, making it ideal for mass manufacturing. Every step of the process, from melting the plastic to extruding the final part, plays a vital role in manufacturing quality plastic parts.
Important stages include:
A clear understanding of these steps helps manufacturers optimize cycle times and reduce defects.
Before plastic can be molded, it must be prepared correctly. Improper material handling can lead to moisture issues, bubbles, or weak parts. This preparation ensures that the plastic resin pellets perform exactly as expected during the molding cycle.
Key preparation steps:
Proper preparation guarantees consistent material flow and higher part quality.
Once the material enters the molding machine, it is conveyed by a rotating screw inside a heated barrel. Here, it is gradually melted and transformed into a uniform molten state.
Accurate temperature control ensures the plastic flows smoothly during injection and prevents issues such as burning or incomplete melting.
The molten plastic is injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. This is one of the most critical stages because it determines the accuracy and strength of the final part.
Key considerations:
Proper filling helps avoid short shots, weld lines, air traps, and uneven surfaces.
After the mold cavity fills, the machine applies packing or holding pressure. This compensates for material shrinkage as the plastic begins to cool.
Benefits of holding pressure:
Consistent packing is crucial for maintaining product strength and structural integrity.
Cooling is the longest phase of the injection molding cycle. The molten plastic solidifies inside the mold, forming the shape of the final product. Cooling efficiency directly impacts manufacturing cost and cycle time.
Core cooling factors:
Faster, uniform cooling results in better part stability and fewer defects.
Once the plastic has fully solidified, ejector pins push the part out of the mold. Proper ejection ensures that parts maintain their shape without warping or deformation.
Important points:
Correct ejection design extends mold life and improves product quality.
Injection molding relies heavily on proper machine settings. Even minor variations in temperature, pressure, or speed can lead to scrap or defects. Maintaining stable process parameters is key to repeatable manufacturing.
Critical machine controls:
Monitoring these parameters ensures consistent performance over long manufacturing runs.
Understanding common injection molding defects helps manufacturers resolve issues early. Most defects originate from improper settings, poor material preparation, or mold design problems.
Common defects:
Preventing these issues requires a combination of correct mold design, proper processing, and regular machine maintenance.
Injection molding is used globally in numerous sectors because of its accuracy, strength, and cost-efficiency.
Common applications:
Its versatility makes it a preferred manufacturing solution for both small-scale and large-scale manufacturing.
Manufacturers choose injection molding for several advantages. It enables high-volume production, reduces per-unit costs, and offers exceptional design flexibility.
Key advantages:
These advantages make injection molding one of the most dependable plastic manufacturing methods in today's world.
Understanding the complete injection molding workflow helps manufacturers improve product performance, reduce defects, and optimize manufacturing cycles. By mastering each stage—from material preparation to cooling and ejection—engineers can ensure consistently high-quality results. This Injection Molding Process Overview serves as a reliable guide for manufacturers aiming to improve their processes and achieve better productivity.
Need Expert Support For Injection Molding? (CTA)
For professional injection molding services, design guidance, or manufacturing assistance, contact our team today: : +1(917)-993-9690 or info@plastic-injectionmolding.com

